Serious environmental pollution and human health issues can arise due to the enhanced utilization of synthetic plastics manufactured from petroleum resources. Therefore, biodegradable polymers (bio-plastics) made from renewable biological materials like natural aliphatic polyesters poly (lactide) (PLA), poly (butylene adipate-co- terephthalate) (PBAT), etc., are considered as eco-friendly plastics that last for a limited period of time in the environment.
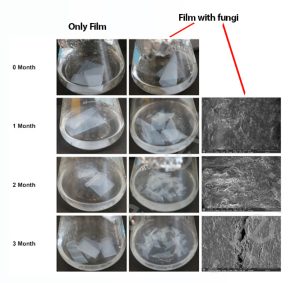
In this paper, Ko et al. have studied the biodegradation of a hydrophilic ternary blend of PBAT-PLA with TPS (thermoplastic starch) by the act of fungal strains at ambient conditions. The surface morphology of the commercial bio-plastic films of PBAT-PLA-TPS was observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The samples were prepared for the SEM analyses by mounting the films on a carbon tape and?coating?them with a 20 nm thickness platinum film using Vac Coat DSR1 ion sputter coater.
The optical and SEM images of the films with or without the fungal strains at different time intervals are shown below.